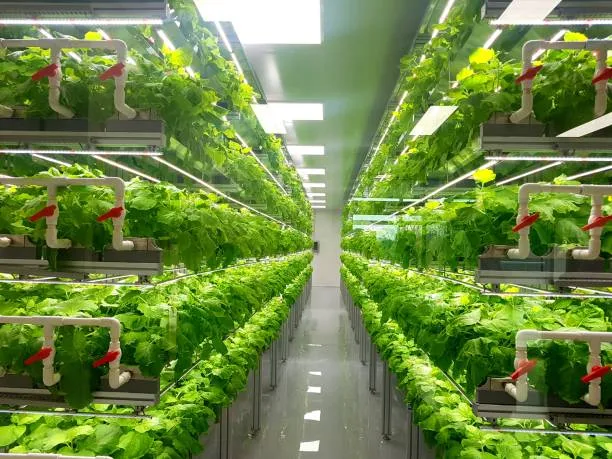
Vertical farming is often seen as a groundbreaking answer to the problems agriculture is grappling with. Its potential for year-round production, saving water, and smart land usage has gained a lot of support lately. But, similar to any technological progress, vertical farming comes with its downsides. In this article, we'll delve into the potential downsides of vertical farming and why it's a significant factor in the future of sustainable agriculture.
The main problem with vertical farming is that it is not as environmentally friendly as initially thought. While the industry claims to be a greener method for growing vegetables, it turns out that the energy used by LED lights used in vertical farms results in higher CO2 emissions than vegetables grown in open fields and then transported over long distances. to reach their destination.
 |
| Photo Credit: Wirestock |
What Is Vertical Farming's Fatal Flaw?
How to Fix vertical Farming fatal flaw?
Identifying the Fatal Flaws:
- High Energy Costs: Vertical farms rely heavily on LED lights to simulate sunlight, which can lead to high electricity bills. As energy prices rise, this becomes a significant financial burden.
- Expensive Infrastructure: Constructing a vertical farm requires a substantial initial investment. The cost of building or renovating a space and equipping it with the necessary technology can be prohibitive.
- Market Viability: The produce from vertical farms, such as leafy greens and herbs, often costs more at the grocery store. If consumers are not willing to pay the higher price, the farm may not be sustainable.
Solutions to Address These Flaws:
- Energy Efficiency: Implement energy-saving technologies and practices to reduce electricity consumption. This could include using more efficient LED lighting or integrating renewable energy sources.
- Cost Management: Explore ways to reduce the initial setup costs, such as using modular designs or cost-effective materials. Seek government grants or subsidies that support sustainable agriculture initiatives.
- Consumer Education: Educate consumers about the benefits of vertical farming, such as the environmental impact and the freshness of the produce. This may justify the higher price point and create a loyal customer base.
- Diversification: Expand the variety of crops grown to include those with higher market demand and profitability. Research and development can help make growing a wider range of crops feasible in a vertical setting.
- Operational Efficiency: Continuously monitor and optimize farm operations to reduce waste and improve productivity. Use data analytics to make informed decisions about crop cycles, nutrient delivery, and other critical factors.
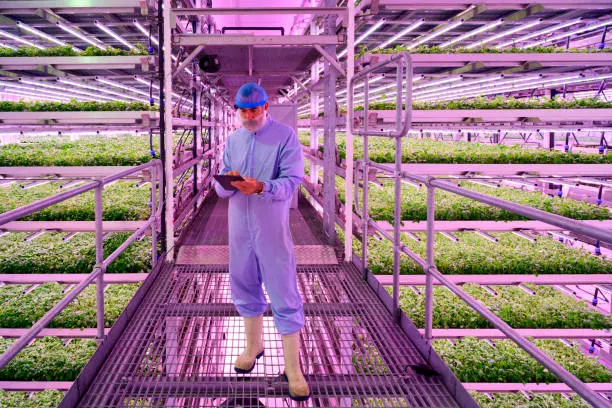
Revolution of Vertical Farming
The vertical farming revolution is about the creative way of planting crops in layers on top of each other, usually in places like buildings or warehouses where the conditions can be carefully controlled. This method of farming is gaining popularity as it offers a sustainable solution to the challenges faced by traditional agriculture.
Key Aspects of Vertical Farming:
- Space Efficiency: By growing crops in vertical layers, this method significantly reduces the amount of land needed for cultivation. It's particularly beneficial in urban areas where space is limited.
- Controlled Environment: Vertical farms are often equipped with advanced climate control systems, allowing for optimal growth conditions year-round. This means crops can be grown irrespective of the external weather conditions.
- Water Conservation: These farms typically use hydroponic systems that circulate water, reducing water usage by as much as 95% compared to conventional farming methods.
- Reduction in Transportation: Since vertical farms can be established close to urban centers, the distance food needs to travel from farm to consumer is greatly reduced, which lowers transportation costs and carbon emissions.
- Pesticide-Free Crops: Growing crops indoors in a controlled environment reduces the need for pesticides, leading to healthier and cleaner produce.
Challenges and Limitations:
- High Initial Costs: Starting a vertical farm can be quite expensive because it needs a lot of money to be spent on buildings and advanced equipment.
- Energy Consumption: The artificial lighting and climate control systems used in vertical farms consume a considerable amount of energy.
- Crop Variety: Currently, vertical farming is most effective for producing leafy greens and herbs. Expanding to a wider variety of crops, including those requiring more space or soil, is still a challenge.
 |
| Photo Credit: JohnnyGreig |
The Future of Vertical Farming
The future of vertical farming is shaping up to be an exciting and innovative field that could significantly alter our approach to agriculture. As urban populations swell and arable land becomes scarcer, vertical farming offers a promising alternative by enabling crop cultivation within urban environments, using vertically stacked layers. This method is not only space-efficient but also allows for year-round production in a controlled environment, irrespective of external weather conditions.
Advancements in technology are expected to drive the growth of vertical farming. The integration of artificial intelligence, automation, and data analytics will likely make these systems more efficient and cost-effective. Moreover, vertical farming's ability to use significantly less water and eliminate the need for pesticides positions it as a sustainable agricultural practice.
However, challenges such as high energy demands and the need for substantial initial investments must be addressed to ensure the widespread adoption of vertical farming. As solutions to these challenges emerge, we can anticipate vertical farms becoming an integral part of the urban landscape, contributing to food security and reducing the environmental impact of traditional farming methods.
Conclusion
Reference & Resources
(1) What Is Vertical Farming's Fatal Flaw? - Green Matters https://www.greenmatters.com/big-impact/vertical-farming-fatal-flaw
(2) Vertical farms are part of ‘the new agricultural revolution https://insights.figlobal.com/sustainability/vertical-farms-are-part-new-agricultural-revolution-how-sustainable-are-they
(3) How vertical farming reinvents agriculture - BBC https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20170405-how-vertical-farming-reinvents-agriculture
(4) What Is Vertical Farming's Fatal Flaw? - Green Matters https://www.greenmatters.com/big-impact/vertical-farming-fatal-flaw
(5) Vertical Farming Has Found Its Fatal Flaw | WIRED UK https://www.wired.co.uk/article/vertical-farms-energy-crisis?linkId=194732677
(6) Vertical farming – is this the future of agriculture? https://climatechampions.unfccc.int/vertical-farming-is-this-the-future-of-agriculture/
(7) Vertical Farming for the Future | USDA https://www.usda.gov/media/blog/2018/08/14/vertical-farming-future

.png)


.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)



0 Comments